automotive radiator
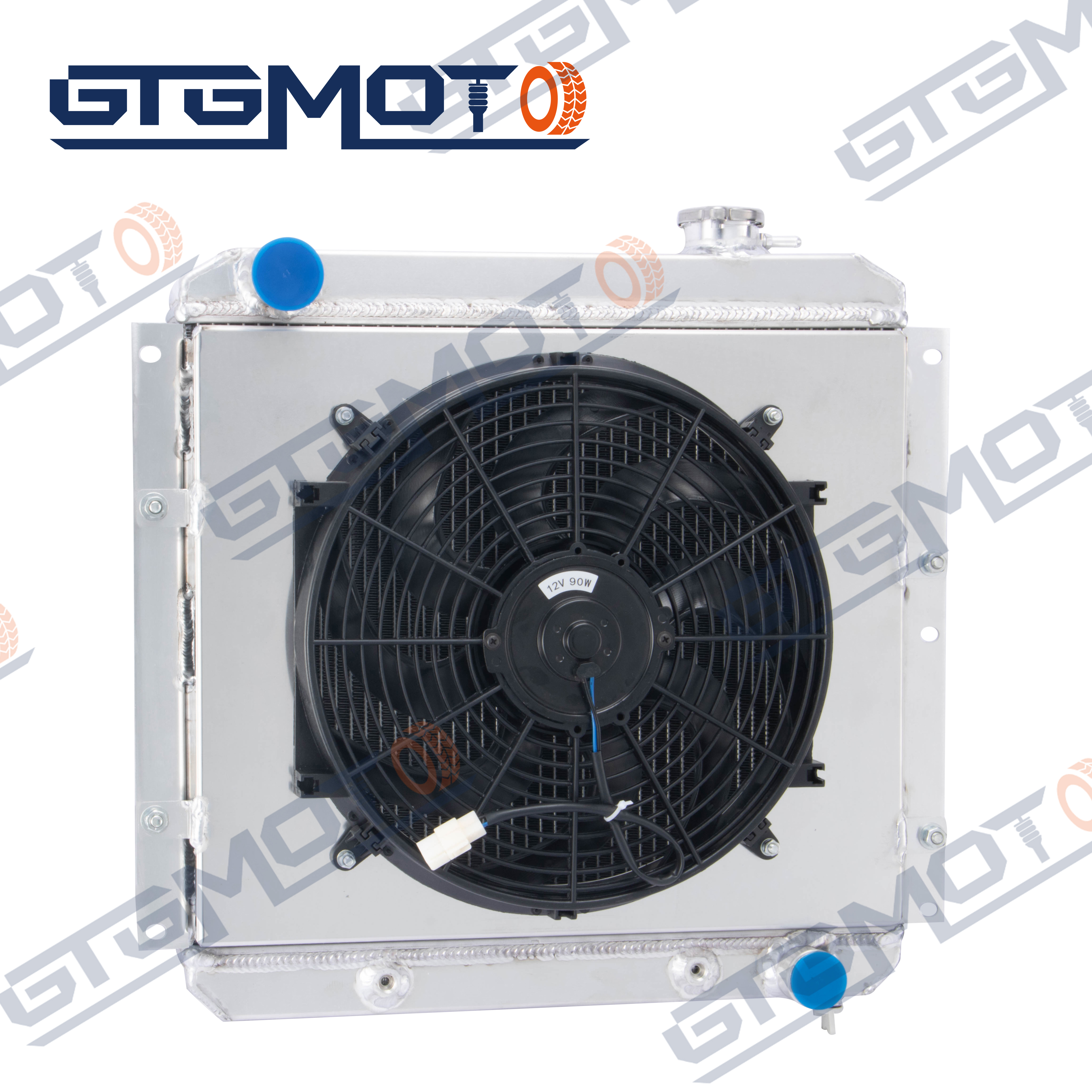
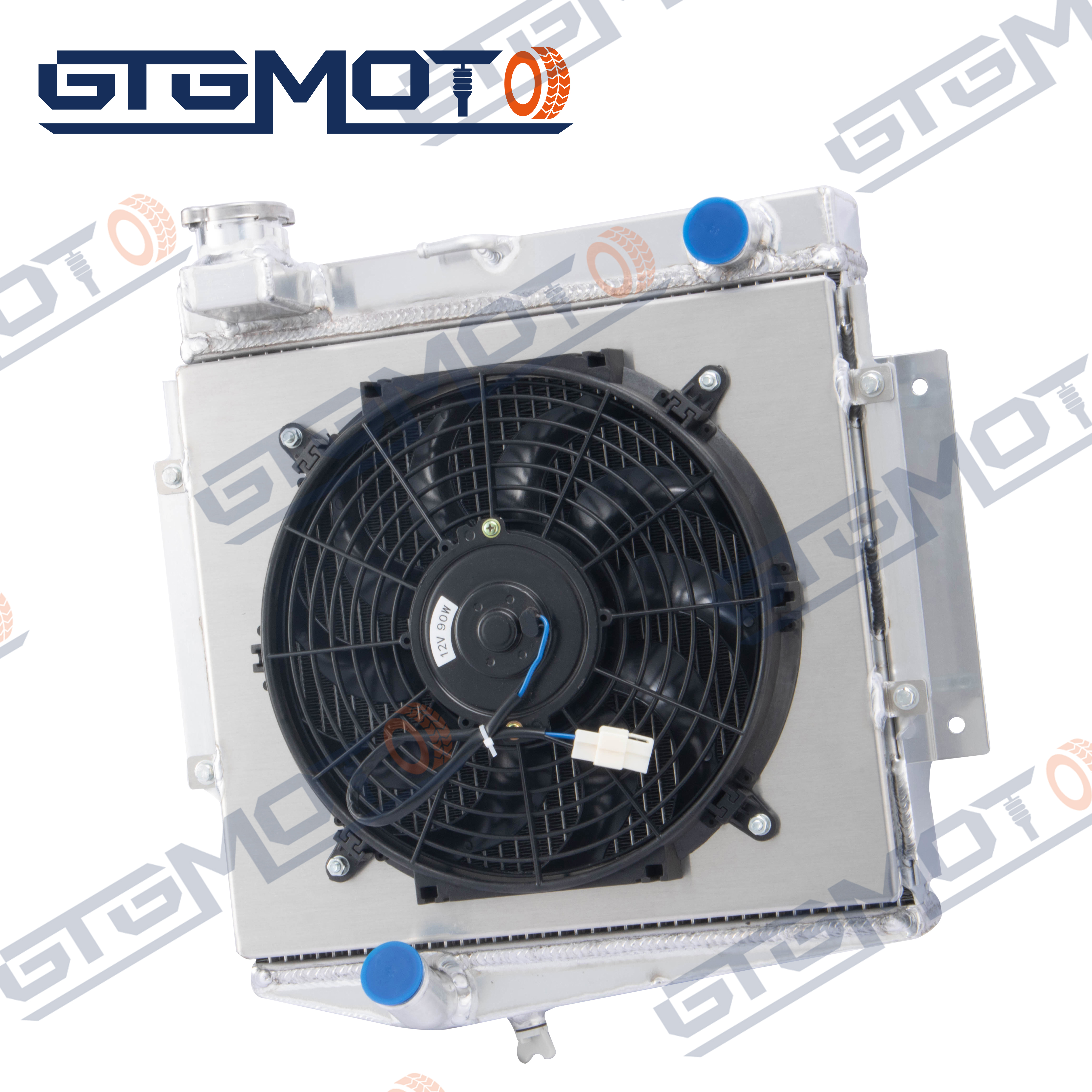
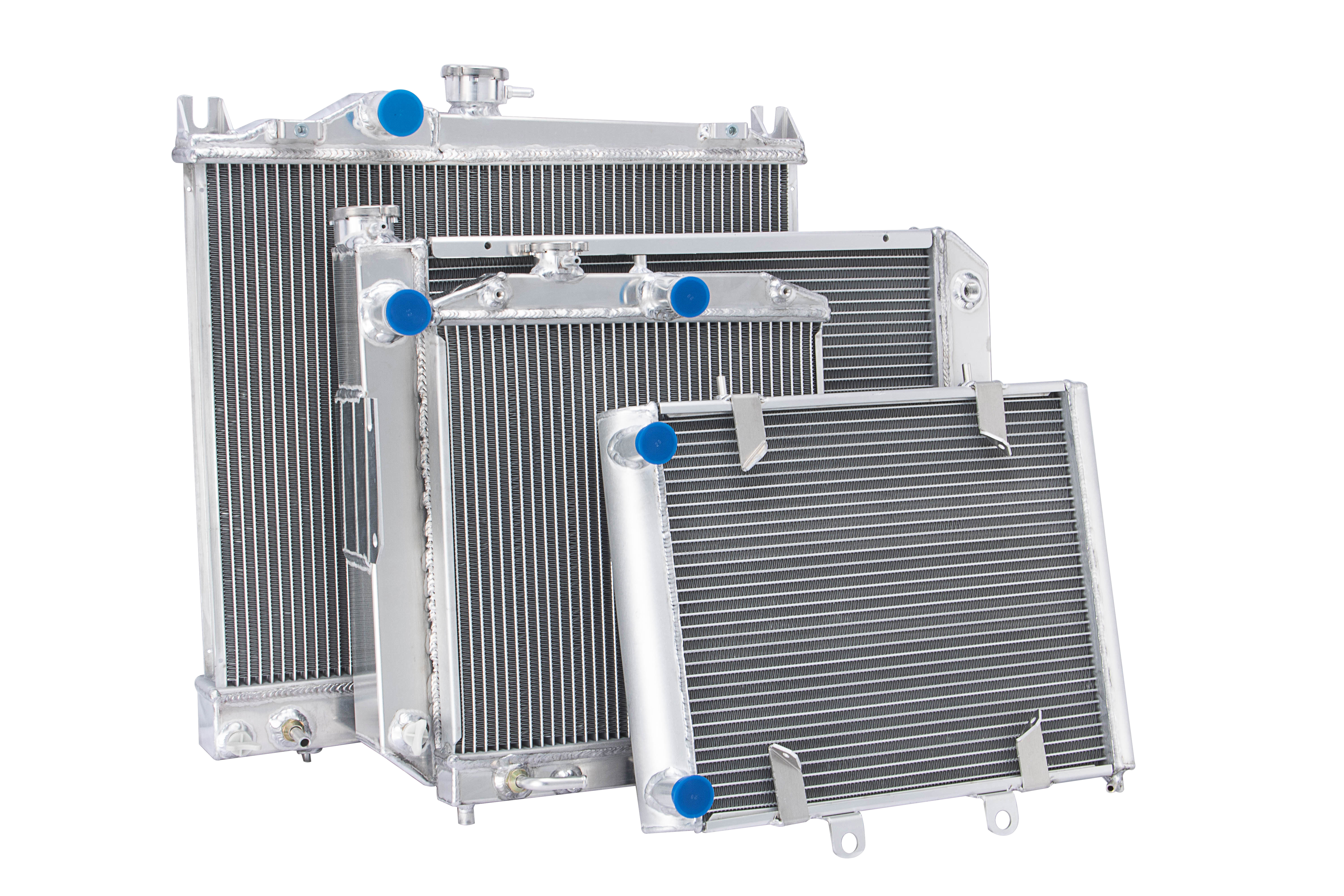
An automotive radiator is a critical component of a vehicle's cooling system, designed to regulate engine temperature and prevent overheating. This heat exchanger uses a combination of coolant fluid, air flow, and specialized materials to maintain optimal engine operating temperatures. The radiator consists of tubes containing coolant fluid, which absorbs heat from the engine, and fins that increase surface area for heat dissipation. As the vehicle moves, air passes through these fins, cooling the fluid before it returns to the engine. Modern automotive radiators typically feature aluminum construction for improved heat transfer efficiency and reduced weight, though some older models use copper and brass. The system works in conjunction with other components like the water pump, thermostat, and cooling fans to maintain consistent engine temperatures. When properly maintained, a radiator helps prevent engine damage, ensures optimal performance, and contributes to fuel efficiency. The design has evolved significantly over the years, incorporating advanced materials and technologies to handle increasing engine power outputs and efficiency demands.