coolant radiator
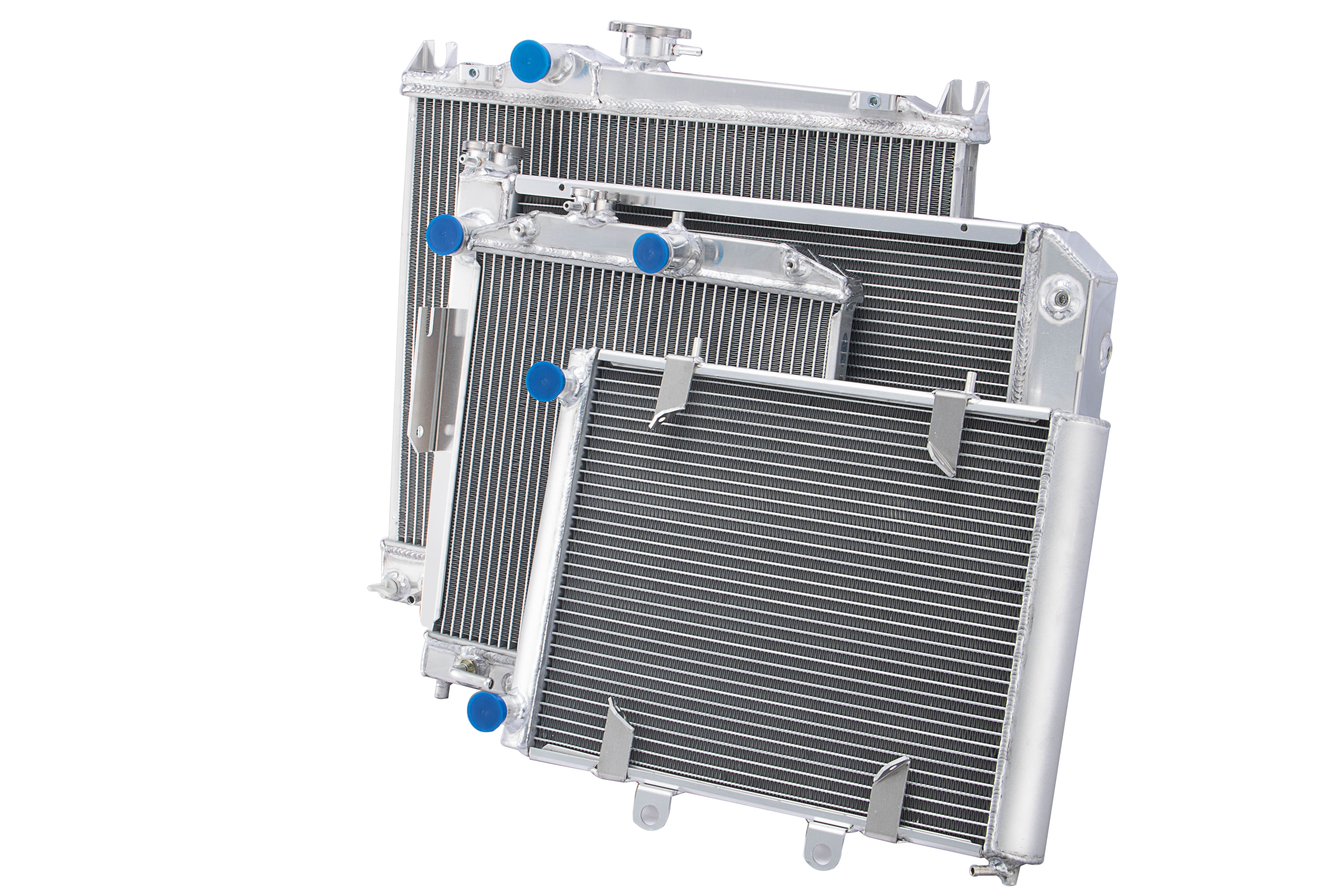
A coolant radiator is an essential component in modern cooling systems, serving as a critical heat exchanger that maintains optimal operating temperatures in various applications. This sophisticated device works by circulating coolant through a network of tubes and fins, efficiently transferring heat from the coolant to the surrounding air. The radiator's design typically features aluminum or copper construction, materials chosen for their superior heat conductivity and durability. Within the radiator, coolant flows through numerous small tubes surrounded by fins that increase the surface area for heat dissipation. A fan system often accompanies the radiator, forcing air through these fins to enhance cooling efficiency. The radiator's core consists of parallel tubes connected by header tanks at each end, creating a continuous flow path for the coolant. Modern coolant radiators incorporate advanced features such as multi-pass designs, optimized fin spacing, and precise flow control mechanisms. These radiators find applications across various industries, from automotive and industrial machinery to power generation and HVAC systems. The size and configuration of coolant radiators vary depending on the specific cooling requirements, heat load, and space constraints of each application.